
Бесплатный фрагмент - When Allen Carr’s method failed to help you to quit smoking or how to overcome Your nicotine addiction, how to stop smoking
IDEDICATED TO
The thirty-five years
spent in slavery
to the tobacco companies
To the thirty-five years of my life.
Introduction
Hello, everybody! I wrote this book for you to be HEALTHY!
Let me introduce myself. My name is Andrey, at the time of writing this book I am 49 years old, of which 35 years I spent smoking. I have made countless attempts to kick this addiction, my non-smoking periods lasted from three hours to one-and-a-half-years. I have tried it all:
— reducing the number of cigarettes;
— the “last pack” method;
— reading the book by Allen Carr (I did it twice) and books by other authors;
— and so on and so forth.
Not all of these attempts were painful, but they all ended in a complete fiasco. However, during my “smoking” experience, there were amazing curiosities when, without noticing it, I stopped smoking for a month or two, and most surprisingly, I understood this only when my fellow smokers, with whom I had smoked like a chimney some time ago, told me about it with admiration.
In this book, I want to tell you about everything I have learned about smoking over those 35 years, the desire to be independent of my nicotine addiction arose as soon as I became aware of its existence, but the awareness occurred after a month of only occasional smoking.
There was one reason for gathering the information in this instruction book: I wanted to quit smoking myself. Now I am sharing this information with you.
It took me 4 weeks to type the text of the book. The collection of material, research, surveys, and experiments took place over 5 years.
Let’s get going!!!
1. Why Allen Carr did not help us
Allen Carr “helps” some smokers and they turn into his zealous supporters. Others are partially influenced: even people, who were completely addicted to nicotine yesterday, easily tolerate the absence of cigarettes for a short time (from one to five or ten hours), but cannot refrain from smoking when there are cigarettes around. There are some smokers who were not influenced by it at all. In this chapter, we’ll study the reasons why Allen Carr influences us in different ways, or (in line with the book title) why he doesn’t.
1.1. The first reason. We have a high threshold of suggestibility resistance
Suggestibility is a degree of susceptibility to suggestion, determined by the subjective willingness to be subject to and obey an external suggestive impact. It is an individual personality trait (this is a scientific definition –author’s note).
The essence of this personality trait is this: the whole “easy way to quit smoking” could not change your worldview, acquired instincts, and information stored in your memory. Simply put, you are more difficult to control than those whom he “helped”.
1.2. The second reason. Associations
Association (interrelation) in psychology and philosophy is a naturally occurring connection between individual events, facts, objects, phenomena, or words reflected in the consciousness of an individual and fixed in their memory. In the case of an associative connection between the mental phenomena “A” and “B”, the appearance of the phenomenon “A” in the consciousness naturally entails the appearance of phenomenon “B” in the consciousness (this is also a scientific definition — author’s note).
In relation to solving the studied problem, the “easy way” quit-smoking attitudes could be ineffective for a very simple reason: the word “smoking” isn’t associated with the act of “smoking” (inhalation of smoke from lit cigarettes). Why? There are many reasons.
— For some people, this could be due to the fact that they previously argued about their not smoking. Try and remember if you’ve had any of these situations:
* you told your parents (even as an adult) that you were not a smoker to keep them from getting mad;
* you told others that you did not smoke (for example, at a new job) in order to create an incentive (reason) to quit smoking;
— You call this pastime (smoking) something else.
— You have long considered smoking shameful, have wanted to break this addiction for a long time and, at the subconscious level, DO NOT SMOKE (it means you do not admit it to yourself). Well, there are such strange cases.
— Other reasons similar to the above.
So, in order to exclude the possibility of the existence of this reason, the action of “smoking” hereinafter will be referred to as the “inhalation of smoke from lit cigarettes”.
1.3. Passive smoking
Passive or secondhand smoking is a very tricky thing, and my gratitude goes to the government that has passed new laws prohibiting the inhalation of smoke from lit cigarettes in public places, or rather from exhaling them. The consequences of secondhand inhalation of smoke from other people’s lit cigarettes are very harmful, even more harmful than the inhalation of smoke from a lit cigarette in your hand.
What’s insidious about passive inhalation of smoke from lit cigarettes is that people who do not have a nicotine addiction become nicotine addicts, gradually, day after day inhaling other people’s tobacco smoke. That’s when it seems as if one cigarette could push a person to become a regular smoker, but in reality, it did not happen in one day or all at once. Secondhand smoking (inhalation of smoke from lit cigarettes) quickly brings ex-smokers back to their addiction.
1.4. Individuality
Allen’s book is good, but it does not take into account individual aspects of addiction and the reasons why, in our opinion, we shouldn’t smoke (inhaling smoke from lit cigarettes).
1.5. How to heal from tobacco addiction (the need to inhale smoke from a lit cigarette)
Let’s find out why we still inhale smoke from lit cigarettes. Just like in the “Easy Way to Quit Smoking”, we will influence ourselves carefully, but through many different information reception channels that are used by our consciousness and subconsciousness. We will change our physical condition (reduce the effects of inhaling smoke from lit cigarettes) even before we get rid of our nicotine addiction. This will be done by accounting for a person’s individuality, i.e. each of us will focus their attention on their own features of addiction.
2. Why we constantly want to inhale smoke from lit cigarettes
2.1. The primary reason is dopamine
Dopamine (DA) is a neurotransmitter produced in the human brain, its production is localized in the hypothalamus. Dopamine is synthesized from the amino acid tyrosine through a subsequent step of L-dioxyphenylalanine. Then, noradrenaline can be produced from dopamine (also in the hypothalamus). Artificially synthesized dopamine, injected into the blood, acts as an activator of cardiovascular activity along with noradrenaline, but this hormone barely penetrates the central nervous system via blood due to the blood-brain barrier (this is also a scientific definition — author’s note).
Dopamine is one of the chemical factors of internal reinforcement (FIR) and serves as an important part of the brain’s “reward system”. Dopamine induces feelings of pleasure (or satisfaction), which affects the processes of motivation and learning. Dopamine is naturally produced in large quantities during subjectively positive experiences such as sex, eating tasty food, and from pleasant bodily sensations. Neurobiological experiments have shown that even reward memories can increase dopamine levels, which is why this neurotransmitter is used by the brain to assess and motivate, reinforcing actions that are important for survival and procreation.
Synthetic analogs. The influence of drugs on dopamine levels
Like most neurotransmitters, dopamine has synthetic analogs as well as stimulators of its release in the brain. In particular, many drugs increase dopamine production and release it into the brain by 5—10 times higher than normal, which allows drug addicts to get a feeling of pleasure through artificial means. Thus, amphetamine directly stimulates dopamine release, affecting the mechanism of its transmission. Other drugs, such as cocaine and some other psychostimulants, block the natural mechanisms of dopamine reuptake, increasing its concentration in the synaptic space. Morphine and nicotine imitate the action of natural neurotransmitters, while alcohol blocks the action of dopamine antagonists. If a patient continues to overstimulate his “reward system”, the brain gradually adapts to the artificially increased dopamine levels, producing less hormone and decreasing the number of receptors in the “reward system”. This is one of the factors that induce an addict to increase the dose to obtain the same effect. Further development of chemical tolerance may gradually lead to metabolic disturbances in the brain and potentially cause serious damage to brain health in the long term.
To illustrate the effect of nicotine on dopamine levels, let’s take a look at their interaction in a graph. Pay particular attention to the yellow line “Degree of dependence on dopamine level stimulation by nicotine”.
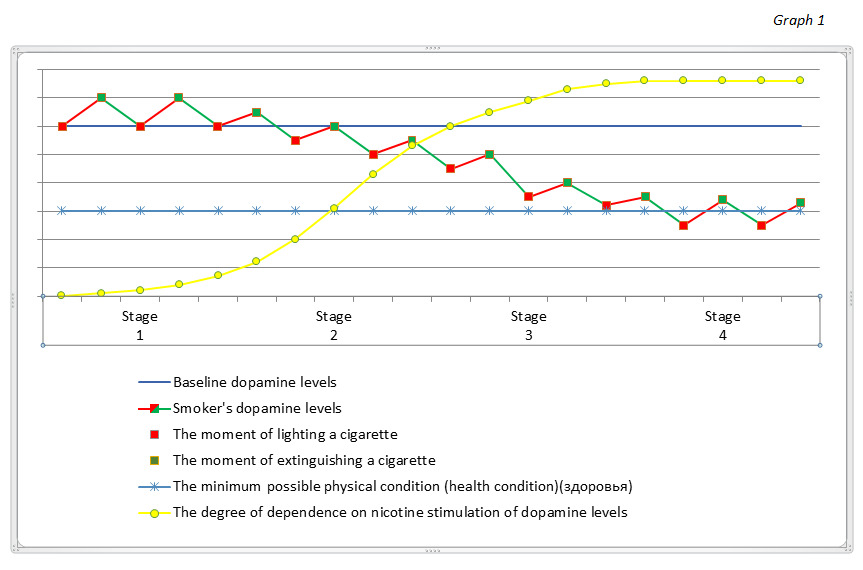
Notes to Graph 1.
— Stage 1 begins from the moment of inhaling smoke from that first cigarette or the first instance of secondhand smoke until the first signs of addiction (the appearance of an unconscious rare desire to inhale smoke from a lit cigarette). The duration of the first stage is from one day to a month, depending on the frequency of intake of smoke from lit cigarettes into the human body.
— Stage 2 shows a pronounced, sometimes not yet realized nicotine dependence, which consists of the systematic inhalation of smoke from lit cigarettes (probably, not so frequent — more than once a week), without any noticeable (or pronounced) deterioration to your health. This stage can last for several years.
— Stage 3 shows pronounced features of health deterioration. The duration of this stage depends on the general state of a smoker’s health at the beginning of the “smoking experience”, lifestyle, physical activity, other bad habits, etc. At this stage, changes have already occurred in the smoker’s character and morality: irritation, grumbling, hatred for others, laziness — traits inherent in most smokers, however, laziness is due to physical weakness.
— Stage 4 shows a significant dependence of dopamine production on the presence of nicotine in the blood with significant health deterioration, when inhalation of smoke from lit cigarettes no longer raises dopamine levels to a level that is acceptable for the psyche. The main feature of this stage: a person wants to inhale smoke from lit cigarettes more and more, but their physical condition already limits the consumption of nicotine, because the body is full of poisons.
Бесплатный фрагмент закончился.
Купите книгу, чтобы продолжить чтение.
