
Бесплатный фрагмент - Mechanisms of cultural evolution

Introduction
The book attempts to reconstruct the milestones of the evolutionary path that the Primate species Homo sapiens followed to create civilization. The final stage of the evolution of this species was cultural evolution, which turned it, which did not have any significant morphological advantages, into the dominant species on the Planet earth.
This became possible because the final stage of the evolution of Homo sapiens did not occur as the evolution of other species — due to the creation of some morphological advantages (fast legs or sharp fangs) for themselves, but due to behavior modification. Behavior modification became possible with some brain structure that appeared in our ancestors. The evolution of the brain provided, in the long run, great advantages for the species in survival and reproduction.
Upsetting some, I still have to declare that man is not a divine creation, and did not even descend from a monkey, he is an advanced primate, whose behavior is regulated not only by the system of instincts created by genetics, implemented through the structures of the brain, but also by the second system on top of the first genetic, a functional system, but also implemented by brain structures.
In other words, for a person we have a control system with two control loops nested one into the other. Such control systems in regulation theory are called systems with subordinate regulation. The inner loop output serves as the input to the outer loop. In simple words, this means that cultural evolution takes place taking into account the existing morphology and instincts of the species Homo sapiens.
The external control loop is formed by functional brain regulators MEMs, which determine the mentality of a person and are often factors that restrain instinctive (genetic) behavior. But this inhibition is not observed in all cases, not in all individuals, and not always. Therefore, you have to look at a person from two points of view in order to better understand him — from the socio-cultural and biological.
Human societies are populations subject to natural selection, capable of inheriting acquired cultural achievements. Note that a person on a desert island cannot evolve culturally. Only societies can evolve, just as populations evolve in biology, not individuals.
Evolution, including cultural, must have 3 indispensable attributes inherent in the biological evolution of any living object. For biological evolution, these are species variability, selection and inheritance.
Genes provide for variability and inheritance, and Darwinian selection weeds out nonviable specimens. Genes are replicators in biological evolution.
The cultural evolution of social behavior, like any evolution of living things, must also have these attributes.
Since the genes that serve as replicators of the entire biological evolution cannot fix the beneficial changes acquired during life (this is a postulate of genetics), it must be admitted that the observed cultural evolution of a person, apparently, occurs with the help of other replicators (MEMs) and another inheritance mechanism.
It should be mentioned that there is no evolution of culture in itself. Culture is inanimate and cannot evolve. The fading of colors over time in the artist’s painting cannot be called the evolution of culture.
Only the expression «human cultural evolution» makes sense.
We have yet to give a definition of culture, since no one has yet proposed such a definition (adequate).
For the first time, a generalized concept of culture is formulated in the book, mechanisms of human cultural evolution are proposed, where MEMs are replicators, the totality of which is phenotypically manifested as a mentality that creates a psychological portrait of a person, determines the way of his thinking and, ultimately, determines his behavior in specific conditions. In other words, mentality is considered as the phenotype of the entire complex of human MEMs.
This approach to cultural evolution makes it possible to build some models of the behavior of local societies, carefully applying the schemes of population genetics.
Sociology studies the behavior of people in large and small societies. This is done purely empirically. No basis other than philosophical conjectures has been laid as a basis, which is important for the practice of science. The founders of this science began to develop from scratch, not taking into account that Homo sapiens is one of the primate species undergoing a stage of cultural evolution.
Since philosophers have penetrated into this science, they raise as the most important naive, meaningless questions: «Are people able to control the conditions of their own lives, or are their actions a consequence of the influence of external social forces? Is society a product of human action?»
The influence on human behavior of genes, upbringing, education and the social environment is considered differently by different schools of sociologists. But unambiguous answers to these questions can be offered by sociobiology. It is she who should become the basis of sociology in order to fill the desert between biology and sociology.
Human societies (societies) are only biological objects that develop over time under the influence of selection, like all other species of living nature, and inheritance is an integral part of this development. Man and societies are part of biological evolution, which claims that all living objects in nature originated from one original living object.
The idea of evolution cannot be considered only one of the hypotheses explaining the world order, as stubborn creationists preach. This is the only reasonable theory that allows you to combine the available information about the life of different creatures at different times.
Even Pope John Paul II announced in an appeal to the Catholic Church that the Vatican agreed to transfer Darwin’s evolutionary teachings from the category of hypotheses to the rank of scientific theory. In his speech, the Pope recognized it acceptable to believe that the human body is the result of evolution.
If you recognize these obvious statements, then discussing the turns of the evolutionary path of societies should be based on evolutionary theory, and not philosophical and moral and ethical ideas, because they are different for different people or groups, are adaptations of culture to the situation at certain points in time and therefore change along with the furnishings.
The conclusions, as a result of this type of discussion, will be different by different researchers.
In science, the conclusions drawn by scientists on the basis of the presented experience should be the same. If some scientific theory does not allow making unambiguous conclusions, then the theory is considered unsatisfactory.
For example, if some issues of intracellular development are considered, then the conclusions of American and Russian scientists will be in agreement, but if issues related to social development are considered, i.e. development with the participation of many multicellular organisms of the species Homo sapiens, there is usually no agreement.
No, because the researchers are on different platforms and have different points of view. If we discuss social issues from one universal platform of sociobiology, then the differences can be overcome as a result of discussion. Therefore, I propose a unified platform for discussing social issues. But there are many influential opponents of convergence of views who parasitize on this difference.
Modern man is the result of evolution. This does not mean a call to equate a person with animals, but reminds that all living organisms and even worms have a structure programmed using the same universal genetic code, all have a cellular structure and each cell has a nucleus with a set of genetic material in it…
The difference in behavior between humans and other species is not caused by a person’s upright posture or his ability to work hard. The difference is caused by the presence of an additional, advanced in cultural evolution, regulation system (external regulation loop) that uses the properties of the brain.
Changes in behavior, due to cultural evolution, made the species Homo sapiens the dominant species on the planet, allowed the creation of civilization.
Why do you need to write a book that popularizes biological tools for dealing with social problems of society?
The fact is that now the problems of society are considered from the standpoint of philosophy, humanitarian concepts, and so on. Such a traditional approach was developed in the course of the historical development of man, and this seems to indicate the validity of its application.
Traditions are an important element of the mechanisms of inheritance in cultural evolution, but they cannot be the basis of modern scientific ideas.
The time has passed when I. Newton called his great book with an exposition of mechanics «Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy» (1684—1686). This name is a tradition of deep antiquity. There is no longer any philosophy in his book. Newton combined separate information about mechanical phenomena, partially revealed before him («I stood on the shoulders of giants» wrote Newton) into one integral theory, held together not by philosophical language, but by mathematical one. Later, many naturalists followed this path, refusing to philosophical verbal descriptions of reality.
However, 200 years after Newton, two «wise men» published the «Communist Manifesto» calling, on the basis of some philosophical ideas, to take up the modernization of social relations in human society.
Their philosophical ideas had nothing to do with biological concepts. They believed that human societies resemble plasticine, from which you can sculpt anything. A similar idea of the possibility of constructing social relations according to the wishes of the elite has survived in Russia to this day. These ideas became widespread in different societies, led to bloody revolutions and numerous victims.
The book shows that there is a big difference in biological and engineering design. In biological engineering, there are no drawings or sketches of the final result. Structures are created, but nobody knows the end result. Structures are alive from the moment they appear and remain so during ontogenesis. Responsibility for biological design rests with everyone involved, not with the manager, as in the case of engineering projects.
The process of creating a human body is controlled not by some separate parts of the embryo, but by the system as a whole. A living system must remain alive all the time, without shutdowns for repair or reconstruction. The systems of a multicellular organism have a certain autonomy, they are not controlled from a single center.
States and individual societies, consisting of living people, themselves should be considered as living organisms with their own needs and capabilities. Social life is linked by many successive chains, and breaks in some of them lead to the destruction of parts of the system, which can be fatal for the entire system as a whole. Still, social systems are more resilient than a house of cards. They have some plasticity, adaptability to external influences.
The ruling elites sometimes propose solutions, ostensibly for the benefit of society, to replace individual building blocks with others, believing that social systems can be rebuilt in this way.
But since the systems are alive, even the noble aspirations of reformers who do not take this fact into account can lead to an undesirable result. Specific examples of such unreasonable behavior are considered in the last chapters on the examples of reformatting the Russian Empire.
1. Human, brain, mind
The emergence of Homo sapiens
Somewhere in southern Africa, about 160—180 thousand years ago, another species appeared in the hominid family of a large order of primates, which biologists gave the name Homo sapiens. This species, not distinguished by any physical qualities, as a result of its unusual evolution, became the dominant species on the Planet. The appearance of new species, as well as their disappearance, are ordinary events in the long evolution of living nature, which has been going on for 3.8 billion years. But in this case, a species arose that turned into a person, became the dominant species, affecting the entire ecosystem. In his development, man went beyond the Earth and acquired the ability to destroy all life on Earth with one careless movement.
The uniqueness of the evolution of this species lies in the fact that it began to evolve differently from all other species, adapting to environmental conditions due to morphological changes, i.e. by changing the structure of individual organs. He didn’t grow hair to keep warm in cold climates, he didn’t grow strong claws like those of predators, his legs didn’t become too fast to flee from predators.
In order not to freeze, he built housing and acquired clothing from skins, created tools for labor and hunting, used fire, which was used even before the appearance of this species, by his distant ancestors. He lived in small, friendly collectives, connected by social relations, where he had to communicate a lot, make primitive tools of labor, develop tactics of collective action, thereby ensuring greater security for himself.
As a result of evolutionary development, he acquired a developed language of communication and an advanced mind, which helped him to survive in difficult and hostile conditions. Language and reason, have a common basis, influence each other and determine the direction of evolutionary development.
This evolution of Homo sapiens, evolution through adaptation of behavior, not morphology, has been called human cultural evolution.
The exit from Africa of Homo sapiens and the development of other continents in time is shown on the map:
(http://www.bradshawfoundation.com/journey)
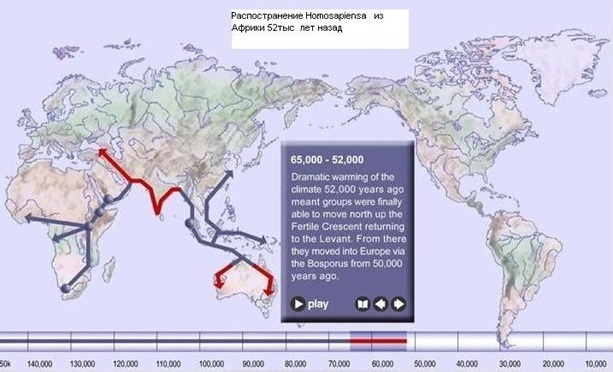
Homo sapiens originally lived in small hunter-gatherer tribes. Life in tribes requires constant communication. In the presence of a large brain potential, this led to the development of a fairly informative language of communication. Not being endowed with special physical qualities, representatives of the species Homo sapiens were forced to make tools for hunting and everyday life. The genetically determined feature of the brain morphology of this species has created a great potential for the development of the mind. The ancestor’s brain of this species has grown 3 times in 2 million years.
Economic activity contributed to the realization of this potential, and the development of reason increased the effectiveness of all activities.
There is a positive feedback (PIC) between the result of work and the increase in intelligence. The mind increases the efficiency of work, and creative work develops the mind. Such positive feedback processes lead to rapid evolution in this direction.
You can read more about the origin and evolution of man in the book by A. Markov (Evolution of man. In 2 books. 2011). This book is based on research in anthropology, genetics, and evolutionary psychology.
We are not interested in genetics, not biological evolution, but in the unique path of human cultural evolution, which made it possible to create civilization.
Brain and Mind
The ancestral brains of Homo sapiens grew enormously over a relatively short period of evolutionary time. Three million years ago, the volume of the skull of an adult Australopithecus was 400—500 cubic meters. cm. Two million years later, his supposed descendant, Homo erectus, had a brain with a volume of about 1000 cubic meters. cm.
Over the next million years, it increased to 900—2000 cubic meters. cm. in modern Homo sapiens.
But the brain is not yet the mind. Brain architecture and environmental pressures work together to create intelligence.
The most important factor that made human cultural evolution extremely effective is the appearance of sufficient intelligence in Homo sapiens in the course of evolutionary development.
By reason, I, to talk about cultural evolution, I mean:
The ability to build in the brain such models of fragments of the surrounding world that allow predicting some events of reality without performing the experiment itself.
The ancestors of Homo sapiens already had intelligence, it is clearly manifested in the behavior of many species of animals, but its further growth stopped at a certain level, not allowing other species to further advance along the path of cultural evolution.
The ancestors of Homo sapiens already had intelligence, it is clearly manifested in the behavior of many species of animals, but its further growth stopped at a certain level, not allowing other species to further advance along the path of cultural evolution.
The new science — infodynamics — deals with the most general regularities in the processes of transmission, transformation, processing and storage of information.
One of the provisions of this science is that consciousness, thoughts, science itself and other results of human mental activity are secondary reality, i.e. approximate models of the real world.
The model cannot coincide with reality 100%, be the same with it from any point of view. It can only be adequate from a certain point of view.
Models describing the same group of phenomena can have different description accuracy and different range of applicability. For example, the laws of electrodynamics formulated by Maxwell are an example of a model that is remarkable and useful under certain conditions. These laws summarize all information about electrical phenomena, but they are interesting among qualified physicists. They will not be useful to a simple electrician, and even more so to the layman, since there are simpler local representations that are a consequence of Maxwell’s equations.
The human mind builds models by being attached to its own point of view, to its platform from which a person perceives the world. The point of view is formed by those principles and ways of thinking that a person learned at the initial stage of his life. Model representations that a person carries in himself depend on the motivation (orientation) of his mind.
If in childhood you were inspired with the idea of the divine creation of the world, then theological thinking forces you to look at the world from this point of view, where everything is arranged according to the will of the creator, where you cannot doubt the basic principles, you need to explain all phenomena so that they fit into the framework accepted dogmas. Then there is almost no freedom of choice for you. They have already chosen for you. Your mind is motivated in a certain way. Therefore, the religious fanatic and the scientist see the world differently.
The ratio of the brain and mind
The brain is an environment built by genetics from specialized cells called neurons. The brain can perform a number of functions: it collects information about the external environment from the sense organs, from nerve cells about the internal environment, processes information, remembers and, depending on the results, controls behavior.
The brain is able to store processed information for some time. The brain of a newborn already possesses some «Reason» in the sense that information processing programs are already operating in it. But these are programs innate «wired» into it. This is the original firmware of the brain, which is not available to us and therefore, it is incorrect to call it the mind.
Part of the brain is dedicated to the mind. The functions of this part are called consciousness, because we are aware of the nature of the information in consciousness.
The functions performed by the brain are realized by changing the functional states of its individual fragments (local neural networks), just as in a computer only the contents (states) of certain cells change during operation.
The mind does not directly depend on the size of the brain. So an elephant with a huge brain has a mind much smaller than a human. His brain is not adapted to learning as much as the human brain. We can say that the architecture of the elephant’s brain does not allow organizing an effective mind.
We are aware and control only the information that is in consciousness. In the brain, apart from consciousness, there is a space called by S. Freud subconsciousness and unconsciousness. The differences are that the programs of the unconscious are formed earlier, while the subconscious is formed in the processes of upbringing and education.
The subconscious and the unconscious contain and operate with information that is inaccessible to consciousness, but plays an equally important role, performing the functions of automatic (without the participation of the mind) control of individual body functions.
In addition, the unconscious and the subconscious put pressure on consciousness, motivate it. Consciousness controls behavior taking into account the already formed unconscious and subconscious.
Finding reason
Although part of the brain is allocated for the mind, it is not there initially. The mind is created in the processes of adaptive self-organization. These processes are influenced by innate instincts (unconscious), the environment in which a person lives, the processes of education and upbringing that form the subconscious. For the development of the mind, the processes of education and training must correspond to innate properties, otherwise they will be ineffective.
The brain can be compared to a computer. Without programs, a computer is useless. The operating system and suite of utilities are installed under the control of professional programmers. Other programs are installed by the user himself according to his needs. Self-installed programs must be compatible with the operating system.
Reason can be considered a semblance of custom programs with adaptive capabilities. But the mind is not created by programmers (teachers and educators), but arises in the processes of self-organization. Teachers and educators are only helpers in these processes. They should be considered as an external environment in which the mind and subconscious are formed. Education and upbringing are effectively perceived by the body at certain stages of its development. The social environment is essential for the formation of the mind and subconscious.
The formation of the mind takes place in the process of self-organization in a certain social environment.
Some unreasonably believe that the human mind is an innate entity that distinguishes it from other primates. But this is not the case.
There are known examples when a person who grew up in a flock of animals (Mowgli) remains at the same level of development as other representatives of the flock. It is no longer possible to train him to become a full-fledged person, since the right time has been missed.
It is also known that no matter how much you educate the monkey, it can become very smart, but it will not be able to reach the average human mind.
This means that not the mind itself, but the ability to develop is an innate, genetically given property. Ability should be viewed as a window that opens at a specific time period. Whether a person uses this window depends on the person’s environment.
In biological evolution, genes in most cases create a kind of predisposition, but do not rigidly determine the processes.
If we do not take into account the environmental factors, their effect on the development processes in living organisms, then we slide towards genetic determinism, if we ignore the organizing principle of genes, then we take the position of the notorious T. Lysenko. These extremes should be avoided.
Human beings are genetically different from other primates in their ability to develop their minds. Mind is a genetic potential that is timely realized in a person at certain stages of his development. Realizing the potential is a matter of education and upbringing.
The ability to develop the mind distinguishes humans not only from monkeys, but also within human populations, these abilities differ greatly. Representatives of biological species have varying degrees of severity of different characters. It is this variability of characters that makes it possible for selection to work. The remark also applies to reason, which is subject to social selection in a social society. The variability of species according to different characteristics was discovered by Charles Darwin, in this case variability is the difference between people in terms of the capabilities of the brain for functional development.
Real progress comes from those people whose minds are above average. It is possible without a big mistake to assume that there is a threshold value of the mind at which effective innovation is possible. To create conditions for work in science, for a person incapable of it, who does not reach the threshold, is a waste of money. A person is born with some potential for the development of reason, but whether it will be realized in life depends on many circumstances.
In the development of the mind, the role of upbringing and education is very great, but not unlimited. The innate genetic programs of the unconscious (instincts) and the learned programs of the subconscious do not allow all information to be absorbed by the brain. Hence, it is clear that the order in which the material for training is presented is important. Which set of material will be learned earlier will be censored for subsequent assimilation.
Inborn instincts are formed at the earliest stages of ontogenesis. Therefore, the brain of a newborn is not an empty vessel that can be filled with anything. He assimilates something and rejects something that does not take root there.
Information is not copied to the brain. External information signals lead to the reconstruction of information in the brain in the form of functional states of local neural networks. If you still call this process copying, then copying is approximate. Some signals may not be recreated in the recipient’s head, and some recreated may not take root in the brain, displaced by other information.
Everyone has come across this. The authority of the teacher in the eyes of the student increases the degree of assimilation.
It must be remembered that the processes of upbringing and education consist in creating favorable conditions for the student and nothing more. You can only learn something yourself. Reason cannot be bought for money, you have to work on it yourself. Money can only buy «crusts».
Today’s level of intelligence was formed as a result of co-evolution. Biological evolution has created the morphology of the human brain, adapted to significant functional development, filled it with some initial content. Cultural evolution realizes the development opportunities inherent in genetics with the help of social institutions.
If in the process of ontogenesis a brain is created that is not capable of development, then training and upbringing will not be able to correct this deficiency, but they can, apparently, to a greater or lesser extent, make it less noticeable (mask). However, not capable of developing in one direction, the brain can be very suitable for developing in another.
What can you compare with? Apparently with a processor, inside of which a number of connections between the elements are missing or they themselves are of poor quality as a result of a technology violation. Therefore, a computer with such a processor will not work as it should. But it may turn out that he can solve some problems quite successfully.
Based on the above, we can conclude:
Mind is an acquired function of the brain. Therefore, like any acquired property, the mind, according to the concepts of genetics, is not inherited. Only the brain is inherited, its general structure, like the structure of other organs.
Smart dads and moms don’t necessarily have smart kids. As for geniuses, according to the signs «Nature often rests on their children.» This observation corresponds to the ideas of genetics about the peculiarities of the inheritance of properties in the sexual reproduction process. Sex cells that program hereditary traits are formed in a stochastic process (meiosis). This is a real lottery. A bomb does not hit the same funnel twice, and geniuses are not born one after another from a pair of the same parents. This is a piece goods. But all children of the same parents can be talented to varying degrees.
In the Bach family, many generations were musicians, but the brilliant Sebastian Bach had to learn music, like everyone else. He may owe his greatness to his unique genotype. But this is not enough if he himself did not make sufficient efforts to achieve the goal.
The shortcomings of upbringing and education, guiding the process of personality formation at a young age, appear later and are difficult or impossible to correct in the future. The emergence of a correctly oriented mind, as well as the child’s assimilation of certain rules of behavior in society, largely depends on the culture of family relations.
Proper upbringing and education depends on many social institutions operating in society, on the well-being of the social society itself.
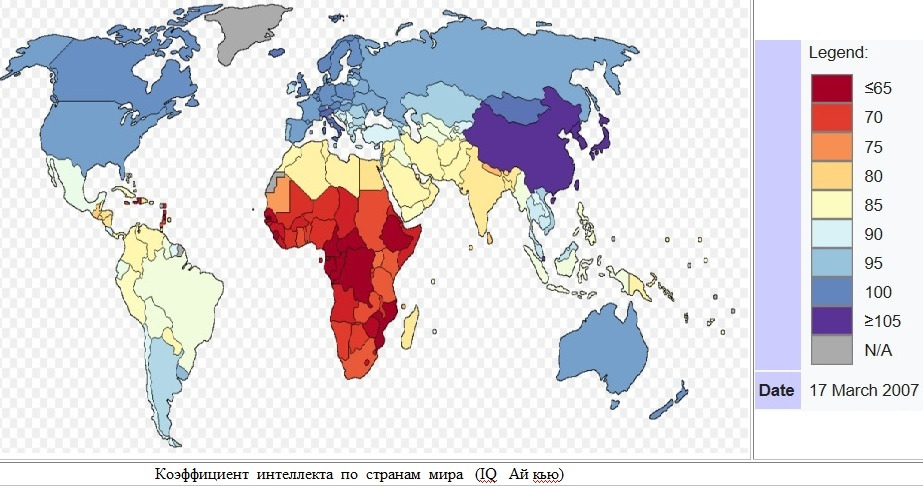
IQ.
Various tests are used to numerically assess the mind. Intelligence quotient (IQ — intelligence quotient, read «aykyu») is a quantitative assessment of a person’s intelligence level (IQ). One of the most famous tests for its determination is Eysenck’s test. Studies have shown that both genetics and the environment affect this indicator. Human races have some genetic differences in this criterion. Asian countries have the highest IQ values: Hong Kong, Korea, Japan, China). Russia and America were in their fifties.
Below is a picture from the book: IQ and the Wealth of Nations — a book published in London in 2000. The book is authored by Dr. Richard Lynn and Dr. Tatu Vanhanen.
Considering the above map, we notice that the most intelligent creature Homo sapiens came from Africa, the continent with the lowest level of intelligence today. Coming out of there, it «grew wiser», evolving in the vastness of Europe and Asia.
IQ by country
Motivation of the mind
Everything that a person perceives from the real world with the help of his senses is reflected in the brain in the form of virtual reality.
An important property of the mind is its orientation. It depends on the social environment in which the mind was formed. The mind can be oriented towards good deeds, unkind or useless. Hence the expression «evil genius». Therefore, it is not enough to characterize a person with the epithet «Smart».
There are many «evil» intelligent personalities in history. Evil in the sense that their minds were directed against the entire society or some part of it.
2. Socialization and cultural adaptation
Methods of cognition
The Homo sapiens species simultaneously used 3 methods of obtaining information.
A practical way based on experience in developing methods of work, assimilating customs and moral values in populations, obtaining other information to satisfy their vital needs.
The religious method of cognition refers to general questions about the structure of the world. Although he gave incorrect (from the current point of view) answers about the structure of the world, it is better than nothing. After all, in ancient times, people began to ask the question — why? The simple answers of religious legends were easily replicated in their heads. So religion conquered the minds, made life easier, grouping people according to faith.
The evolutionary significance of religions consists, in my opinion, in the fact that religions contributed to the emergence of social relations in large communities, restraining aggression in people’s behavior within a certain framework, creating in the minds of people some moral norms demanded by a social society by instilling faith in one or another God, rooting customs, some moral principles by methods of manipulating consciousness.
There are many religions in different parts of the world, where isolated populations of Homo sapiens previously lived, but this only suggests that they were in demand by the logic of cultural evolution, the development of the HS mind and communication languages. All religions have their own gods, their own principles and their own holidays. Religions do not have any consensus on this matter.
The scientific method of cognition, based on experience, which is generalized, gives all knowledge a systematic nature of laws that allows you to make scientific predictions, and as a result, engage in innovative activities: invent technologies and tools for hunting, labor and war. For a long time, the last two methods of cognition did not intersect and coexisted peacefully.
Socialization and reason
Without sufficient reason, without the ability to think abstractly, the scientific method of cognition would be impossible, which means that all innovations are impossible, a high level of technology development, an increase in labor productivity are impossible. A civilization built without advanced intelligence would not be very effective.
Ants are very social insects. They embarked on the path of socialization 100 million before us. years old. They are biologically successful. But their brains are too small to create an effective mind. They have a distributed mind like a community. Socializing individuals without sufficient intelligence has a limited effect.
The mind of one person cannot cope with a difficult task. Big tasks require the consolidated efforts of many separate minds. For thousands of years, stone tools were made by our ancestors, but there was no effective breakthrough. It was not because creative people were disunited, living in small tribes. There was a slow evolution of the mind itself, the methods of hunting, obtaining food, technological methods of making stone tools.
To get results from the work of the mind, you need an appropriate environment, exchange of views with colleagues, and all kinds of creative interaction. If the founder of our Russian science, M. Lomonosov, had not been able to get from his village to Moscow, he would have remained an unknown peasant, plowing the land and repairing clamps, and Moscow University would not bear his name.
The mind in the brain arises in the processes of self-organization. Among savages, reason will be of little demand. There is no demand for it.
All computer microcircuits (hardware) remain motionless until the user turns on the power, thus combining all microcircuits into a single structure. The brain is the same carrier of the mind, as the «hardware» of the computer is the carrier of programs.
Socialization activates the processes of self-organization, strengthens the mind, making it collective, belonging to the entire society. Only the collective mind is able to build a developed civilization.
Living in large settlements (socialization) makes possible the division of labor, which greatly increases its productivity in comparison with labor in subsistence farming. This was noted by the founder of economic doctrine A. Smith in his famous work «The Wealth of Nations».
An increase in labor productivity naturally causes the development of trade, navigation, scientific research and many other areas and activities. At the same time, market relations arise, and the construction of civilization begins.
The transformation of Homo sapiens into a human can be conditionally attributed to the period 6000—10000 years ago. This is the conditional beginning of social (cultural evolution), the point when the constantly increasing speed of cultural evolution has reached a speed that is significant by human standards. Interestingly, church leaders consider the same date as the beginning of the world — when God descended and created everything. And before this date, nothing supposedly happened. But scientists believe that prior to this date, there was biological evolution for 3.8 billion years. Such a «small» difference in world outlook.
The emergence of cultural adaptations
Any evolution of living things consists in adaptation (adaptation) to environmental conditions.
Cultural adaptation is the preservation in generations (inheritance) of information obtained as a result of activity, which changes thinking and behavior.
In biological evolution, genetic inheritance of properties acquired during a lifetime is impossible, which has theoretical and experimental confirmation. Cultural adaptations occur in all mammals due to the presence of a brain. But there is a natural limit that limits the further spread of these adaptations in populations.
The species Homo sapiens managed to overcome this limit. By the way, 50 thousand years ago, there were several other species of great apes, which also managed to overcome the limit, but as a result of natural selection, they became extinct before they survived to this day. The most famous of them are Neanderthals, which represent a separate parallel branch, which are 99.5% genetically identical with modern humans. The evolutionary branches of the ancestors of Neanderthals and modern humans diverged about 500—700 thousand years ago.
It was not labor or walking upright that turned Homo Sаpiens into a man. The most important factors that determined the emergence of adaptations of cultural evolution for Homo Sapiens and his transformation into a man who has become the dominant species on the planet are the following.
1. Achievement of sufficient intelligence by the species of Homo Sapiens as a result of evolutionary development.
2. Socialization of the species, i.e. unification first into tribes, then into large settlements, into cities and states.
Separately, neither reason nor socialization can lead to such a unique result that we have for a person. Eusocial insects (ants, termites, bees, etc.) created their civilizations of a lower level, without sufficient intelligence.
2. Socialization and cultural adaptation
Methods of cognition
The Homo sapiens species simultaneously used 3 methods of obtaining information.
A practical way based on experience in developing methods of work, assimilating customs and moral values in populations, obtaining other information to satisfy their vital needs.
The religious method of cognition refers to general questions about the structure of the world. Although he gave incorrect (from the current point of view) answers about the structure of the world, it is better than nothing. After all, in ancient times, people began to ask the question — why? The simple answers of religious legends were easily replicated in their heads. So religion conquered the minds, made life easier, grouping people according to faith.
The evolutionary significance of religions consists, in my opinion, in the fact that religions contributed to the emergence of social relations in large communities, restraining aggression in people’s behavior within a certain framework, creating in the minds of people some moral norms demanded by a social society by instilling faith in one or another God, rooting customs, some moral principles by methods of manipulating consciousness.
There are many religions in different parts of the world, where isolated populations of Homo sapiens previously lived, but this only suggests that they were in demand by the logic of cultural evolution, the development of the HS mind and communication languages. All religions have their own gods, their own principles and their own holidays. Religions do not have any consensus on this matter.
The scientific method of cognition, based on experience, which is generalized, gives all knowledge a systematic nature of laws that allows you to make scientific predictions, and as a result, engage in innovative activities: invent technologies and tools for hunting, labor and war. For a long time, the last two methods of cognition did not intersect and coexisted peacefully.
Socialization and reason
Without sufficient reason, without the ability to think abstractly, the scientific method of cognition would be impossible, which means that all innovations are impossible, a high level of technology development, an increase in labor productivity are impossible. A civilization built without advanced intelligence would not be very effective.
Ants are very social insects. They embarked on the path of socialization 100 million before us. years old. They are biologically successful. But their brains are too small to create an effective mind. They have a distributed mind like a community. Socializing individuals without sufficient intelligence has a limited effect.
The mind of one person cannot cope with a difficult task. Big tasks require the consolidated efforts of many separate minds. For thousands of years, stone tools were made by our ancestors, but there was no effective breakthrough. It was not because creative people were disunited, living in small tribes. There was a slow evolution of the mind itself, the methods of hunting, obtaining food, technological methods of making stone tools.
To get results from the work of the mind, you need an appropriate environment, exchange of views with colleagues, and all kinds of creative interaction. If the founder of our Russian science, M. Lomonosov, had not been able to get from his village to Moscow, he would have remained an unknown peasant, plowing the land and repairing clamps, and Moscow University would not bear his name.
The mind in the brain arises in the processes of self-organization. Among savages, reason will be of little demand. There is no demand for it.
All computer microcircuits (hardware) remain motionless until the user turns on the power, thus combining all microcircuits into a single structure. The brain is the same carrier of the mind, as the «hardware» of the computer is the carrier of programs.
Socialization activates the processes of self-organization, strengthens the mind, making it collective, belonging to the entire society. Only the collective mind is able to build a developed civilization.
Living in large settlements (socialization) makes possible the division of labor, which greatly increases its productivity in comparison with labor in subsistence farming. This was noted by the founder of economic doctrine A. Smith in his famous work «The Wealth of Nations».
An increase in labor productivity naturally causes the development of trade, navigation, scientific research and many other areas and activities. At the same time, market relations arise, and the construction of civilization begins.
The transformation of Homo sapiens into a human can be conditionally attributed to the period 6000—10000 years ago. This is the conditional beginning of social (cultural evolution), the point when the constantly increasing speed of cultural evolution has reached a speed that is significant by human standards. Interestingly, church leaders consider the same date as the beginning of the world — when God descended and created everything. And before this date, nothing supposedly happened. But scientists believe that prior to this date, there was biological evolution for 3.8 billion years. Such a «small» difference in world outlook.
The emergence of cultural adaptations
Any evolution of living things consists in adaptation (adaptation) to environmental conditions.
Cultural adaptation is the preservation in generations (inheritance) of information obtained as a result of activity, which changes thinking and behavior.
In biological evolution, genetic inheritance of properties acquired during a lifetime is impossible, which has theoretical and experimental confirmation. Cultural adaptations occur in all mammals due to the presence of a brain. But there is a natural limit that limits the further spread of these adaptations in populations.
The species Homo sapiens managed to overcome this limit. By the way, 50 thousand years ago, there were several other species of great apes, which also managed to overcome the limit, but as a result of natural selection, they became extinct before they survived to this day. The most famous of them are Neanderthals, which represent a separate parallel branch, which are 99.5% genetically identical with modern humans. The evolutionary branches of the ancestors of Neanderthals and modern humans diverged about 500—700 thousand years ago.
It was not labor or walking upright that turned Homo Sаpiens into a man. The most important factors that determined the emergence of adaptations of cultural evolution for Homo Sapiens and his transformation into a man who has become the dominant species on the planet are the following.
1. Achievement of sufficient intelligence by the species of Homo Sapiens as a result of evolutionary development.
2. Socialization of the species, i.e. unification first into tribes, then into large settlements, into cities and states.
Separately, neither reason nor socialization can lead to such a unique result that we have for a person. Eusocial insects (ants, termites, bees, etc.) created their civilizations of a lower level, without sufficient intelligence.
3. Cultural evolution of Homo sapiens
About evolution
EVOLUTION — (from Lat. Evolutio — deployment) in a broad sense, a synonym for development; processes of change occurring in living and inanimate nature, as well as in social systems.
This term is used to refer to the entire development process, which consists of fairly smooth periods and sharp revolutionary periods. Sometimes this term is used to name only smooth periods of development.
The idea of evolution cannot be considered only one of the hypotheses explaining the world order. In biology, this is the only reasonable theory that allows you to combine the available information about the life of different creatures at different times.
Prerequisites for the evolution of living things
The prerequisites for the evolution of living nature are as follows:
1. Variability of objects of living nature. Descendants are not clones of the parents and are always different from them in some aspects.
2. Selection. Living objects, being in populations, are forced to fight for limited food resources. Therefore, inevitably there is a struggle with others like themselves or with environmental conditions for vital resources, i.e. the possibility of existence and reproduction. Charles Darwin called these processes natural selection.
3. Inheritance. Those individuals that, by their innate qualities, will be most adapted (adapted) to the conditions of existence, have more chances to survive and reproduce. These qualities in biological evolution are provided by the mechanisms of inheritance.
Charles Darwin established the first two conditions, but he knew nothing about the mechanisms of inheritance. The mechanisms of inheritance were investigated later.
If at least one of these conditions is not met, for some objects, then they do not evolve. Throughout biological evolution, the first and third conditions are met due to the presence of genes in cells, which play a key role in the mechanisms of inheritance.
Genes ensure the inheritance of only innate properties, and not acquired during life.
This is one of the cornerstones of population genetics.
Human cultural evolution has been observed throughout the entire historical period. Its manifestation consists in the accumulation of cultural achievements (adaptations) by humanity, achievements not innate, but acquired. This raises questions about how cultural adaptations arise and where they accumulate and what are the mechanisms of their inheritance. After all, cultural evolution is an observable fact. What plays the role of replicators (from the Latin replicatio, renewal, repetition) in cultural evolution instead of genes?
Evolution without genes
In populations of living organisms, in response to changes in the external conditions of existence, adaptations arise as a result of selection. These adaptations are fixed in genes and transmitted during the sexual process to the next generation, i.e. genes carry out vertical replication, link generations through inheritance.
Adaptation in biological evolution is a change in the morphology of organisms, allowing the body to better adapt to the conditions of existence. At the cellular level, adaptations consist in modifying the genome, which largely programs the morphological features of the organism.
Due to the established mechanism of transmission of adaptations through the sexual process, the restructuring of the morphology of organisms in populations occurs slowly, according to the scale of human life.
The historical process of human development (cultural evolution) demonstrates the development of culture. One culture replaces another, inheriting some of the features of the previous one. These changes occur much faster than the processes in biological evolution.
The presence of the evolution of human culture indicates that three conditions necessary for its course are fulfilled. But inheritance in culture is the inheritance of acquired properties that cannot be carried out with the help of genes. It can be concluded that the observed human cultural evolution, apparently, occurs with the help of other replicators (not genes) and a different inheritance mechanism.
Therefore, we can talk about the cultural (social) evolution of man, as evolution without genes, occurring with the help of other replicators. Over the past millennia, the appearance of new significant morphological changes in a person has not been seen, he has remained the same as he was. All changes in the conditions of existence are determined by the cultural evolution of a person.
Culture and mentality
It is time to define the concept of the term «Culture». You can find many definitions of the phenomenon of culture, which are given by people from different points of view. All these definitions are based on attempts to grasp the common in different types of cultural manifestations.
Another approach is based on defining a culture in terms of how it is inherited. The most convincing is the definition of the remarkable cultural scientist Yu. Lotman:
«Culture is a collection of genetically non-inherited information in the field of human behavior. Art is part of culture along with science.»

The term «mentality» comes from the Latin «mind, thinking, way of thinking, mental disposition», meaning a general mental attitude, a relatively holistic set of thoughts, beliefs, skills that creates a picture of the world in the head. Mentality is both a characteristic of the type of thinking (consciousness) and the subconscious activity of the brain.
A prerequisite for evolution in populations or societies is natural selection. In the cultural evolution of a person, adaptations consist in changing the mentality, which changes (adapts) a person’s behavior in such a way as to adapt it to external conditions, including the social environment.
But cultural adaptations do not arise at birth, but during life with the development of the mind. Since these mental adaptations are not inherited through genes, the question arises as to how they are passed on to subsequent generations. What replicators help this process take place? This issue will be discussed later.
Clarification of the term «cultural evolution»
Please note that it is incorrect to talk about the evolution of culture in itself. Culture is recorded in the form of traces of human activities. Culture is an inanimate substance and cannot evolve as a living one, with the creation of adaptations. The evolution of culture is manifested through changes in the discovered traces of human activity in different eras. If the traces of a person’s activity change, then apparently because the person himself changes, his thinking (mentality) and, as a result, his behavior change.
A person has morphologically changed insignificantly during the historical period, but his «soul» has changed. And speaking in scientific language, the mentality of a person has changed.
When anthropologists talk about changes in the bones of ancient animals from different eras they found, they conclude about the evolution of one or another species, and not about the evolution of the bones themselves. It’s the same with culture. An important clarification is that it is not the evolution of culture, but the cultural evolution of man.
When they start talking about the evolution of culture in itself, they fall into a logical dead end. It is impossible to talk about the evolution of an inanimate entity. And here art historians, philosophers and everyone who joined them are trying to find a way out, talking about the inheritance of elements from different cultures. This is a conversation about nothing. Warm and heavy cannot be combined in one theory.
Some cultural researchers see this incongruity. Cultural anthropologists such as Julian Steward drew attention to the Darwinian concept of «adaptation» in the middle of the 20th century, arguing that all societies must adapt to the environment in one way or another.
Functional adaptations of the brain
The activity of the brain is a change in the functional state of its individual fragments (neurons). The essence of functional changes can be demonstrated using the example of a water tap. The water tap has two positions — «Open» and «Closed». The difference between these two functional states of the crane cannot be determined visually. The tap looks the same in both positions. If you supply water to its input, then the difference in these states will immediately be revealed. The difference manifests itself in the work, i.e. in behavior.
Mentality should be considered as a result caused by all functional states of parts of the brain, both consciousness, subconsciousness and unconsciousness. To a large extent, only the unconscious can be inherited, since it is the result of the work of genes.
Therefore, the mentality can only be partially inherited, and transmitted by genetics to the next generation of the species.
On the mechanisms of creation and preservation of cultural adaptations in the following chapters.
Culture and cultural evolution
From the point of view of sociobiology, culture can be defined in this way.
Culture is a manifestation in human behavior and thinking of a set of functional adaptations of the brain that arose as a result of the historical process of development of the species Homo sapiens, which are transmitted from person to person, from generation to generation in a non-genetic way.
Those who are trying to give a definition of culture that could combine into one group, for example, poetry, ballet and painting, cannot understand that such attempts are not constructive. Many philosophical definitions of culture have been invented, and none of them is meaningful. At the same time, everyone notes the complexity of constructing such a definition.
So you took the wrong side, gentlemen. Human culture can be correctly defined in terms of sociobiology, not philosophy.
It is obvious that cultural manifestations should be united not according to the ways of expressing thoughts, emotions, behavior in them, but according to the way these manifestations are inherited in societies. Culture is the accumulation and manifestation of the development of various aspects of the human personality, and what is common to all manifestations is that they are accumulated and transmitted to subsequent generations in a non-genetic way.
The evolution of culture should be considered as a change in time of the preserved manifestations (traces) of activity in different spheres of the social (living in society) man, just as the change in time of the remains of ancient animals is traces of biological evolution.
The term «culture» in this formulation acquires an expansive meaning, since it covers both science and religious beliefs, as was pointed out by the cultural scientist Yu. Lotman. It is impossible to argue with the fact that humanity is evolving. But not like other primates, not like other species. This is especially noticeable over the past 300 years, when science acquired a systematic character, uniting the islands of knowledge of previous eras.
Human evolution due to functional adaptations of the brain is fast, compared to slow biological evolution, which can therefore be ignored when analyzing the changes that occur in societies. You will not find an adequate definition of the concept of «cultural evolution» anywhere. This expression is replaced by the expression «cultural evolution», as if these are equivalent concepts. It is time, finally, to give the first adequate definition.
Cultural evolution — time-consistent changes in human culture in society, caused by functional changes in the brain. Culture is one shot from the film «Human Cultural Evolution».
In the process of biological evolution, with the appearance of a brain in multicellular organisms, it became possible in it to maintain functional adaptations that regulate behavior. The significance of non-genetic adaptations in humans has increased over time. Finally, evolution on a new trajectory, which led to the development of civilization, made the good old morphological methods of adaptation for Homo sapiens little in demand.
Although the world around us has changed greatly with the development of civilization, the global principles of evolution have been preserved. Now, as before, in order to survive in the World, you need to adapt to it. No other way. Living together in the modern world on one planet Earth, covered by numerous communications, will not work according to your own rules. Everyone needs to adapt in order to live.
Endless talks about unchanged sovereignty for states are manipulations of public opinion, psychological opium for the people. Sovereignty for states becomes limited. A discussion is permissible on the question of how best to fit into this world, with minimal losses for oneself. If, nevertheless, the discussion goes in the wrong direction, then perhaps the next branch of the evolution of intelligent beings will be an inorganic machine civilization.
Differences in human evolution from other species
Some people find it intolerable to realize that man and any kind of monkey have a common ancestor, that man is one of the species of the order of primates. I don’t understand this snobbery. But even among the human tribe, you can find representatives that seem terrible to every civilized person.
When you get to know a person, it is more correct to look not at his distant ancestors, but at what he is today. For a more detailed analysis, you should also pay attention to relatives.
In this section, we will show some of the differences between human evolution and the evolution of other mammalian species. According to the biological classification, it is customary to consider a person to be one of the species of the order of primates, therefore, he must obey the biological laws common to all, but this turns out to be not entirely true.
1. The basic model, which well describes the dynamics of animal population, is the logistic model proposed by the Belgian mathematician Verhulst back in 1838. The logistic curve, which is a solution to the Verhulstom equation, indicates a rapid increase in the number of the species at the beginning and a slowdown when it reaches the ceiling of the ecological niche. Thus, the capacity of an ecological niche is a systemic factor that determines the ceiling for population growth in a given habitat.
The logistic model reflects the dynamics of populations, the number of which, under any initial conditions, approaches with time to a certain stationary value.
Simply put, as long as there are resources for development, the number of this species grows rapidly, but resources are always limited, which causes limitation of the population size. Growth stops. The ecological niche is filled. A biological species is a passive consumer of existing resources.
Demography does not obey this law, although we are typical monkeys in morphology and mathematicians had to invent their own equations for humans that describe the demographic process.
On the models of population growth (http://www.keldysh.ru/papers/2005/prep13/prep2005_13.html)
This suggests that, under the guise of HS, someone has appeared whose numbers do not obey the general rule.
2. The ecological niche, which limits the distribution of any species, is expanded by man and is not a limiting parameter for him.
3. With an increase in the population size, the area occupied by it increases proportionally. So it was with HS. But for some time, people began to crowd into cities.
4. Natural selection is selection, as a rule, individual selection in populations. Different structures (state, private) appear in societies, and along with individual selection, there is also group selection, selection between social structures within states and between different states on the planet. In particular, the class struggle and other types of joint struggle of different social groups for some preferences is a manifestation of group selection.
These processes of group selection cannot be adequately described within the framework of socio-Darwinism, but only within the framework of sociobiology, because this is mental selection, not selection based on morphological properties. For biological systems, group selection is not characteristic, but for human societies it is important.
5. People have created constitutions, laws that guarantee them certain rights. In biological evolution, no one guarantees anyone any rights.
6. The speed of human social evolution is much higher than biological and is still increasing.
The listed changes (deviations from the usual biological evolutionary path) indicate that man has somehow evolved and is significantly different from Homo Sapiens, which appeared 160—180 thousand years ago. But these differences are not genetic. Differences in behavior are caused by functional changes in the states of neural networks, changes in thinking.
Functional changes in thinking are analogous to changes in the software environment in a computer, which give it different qualities.
These arguments are enough to admit that man is no longer an animal and cannot be viewed from a purely biological standpoint. It has evolved. But this happened not with the help of genes, as the evolution of species in biology takes place, but with the help of other replicators and a different mechanism of inheritance.
4. The origins of cultural evolution
For any evolution of living things, energy resources are needed to support the processes of life, and hence homeostasis. The plant world receives energy directly from the Sun, using the reaction of photosynthesis, biological objects for energy must be fed on organic food with energy stored in it. Cultural evolution is human evolution in the field of information processing and needs to be fed by an information resource.
All organic resources are limited, so biological objects are forced to fight for them in different ways. The struggle for coexistence leads to natural selection of individuals in populations, useful adaptations are preserved in populations in the process of inheritance.
The information resource of cultural evolution is essentially unlimited. Having learned how to extract, exchange and use it, a person gains almost unlimited power and significant ecological release. Human actions are no longer fully determined by environmental conditions, there is a certain «free will».
Information resource properties
In real life, when two subjects share resources (voluntarily or as a result of coercion), then the resource increases for one, and decreases for the other. This is a fundamental rule of life following from the laws of conservation of matter. Thanks to this property, competitive relations of living beings for resources arise, and history is the incessant wars of mankind for material resources.
If a person shares an apple with a friend, then he has only half of the apple left for consumption. There must be motivation to share.
Information is also a resource, a resource with special properties.
The donor’s information resource, when shared with others, does not decrease, which radically distinguishes it from any material resource.
If people share an information resource, it makes both of them richer. The mind is a tool that allows information to be used. And it is beneficial to share information, because it makes everyone richer.
The one who received becomes richer because the resource received can be used to his advantage (it is assumed that this is some information and technological resource), and the other, acting as a donor, has a chance to receive a similar resource in the future from the recipient, if between the counterparties have established a relationship of trust.
This property of information resources makes the process of uniting people endowed with sufficient intelligence in large agglomerations (the process of socialization) beneficial and evolutionarily inevitable, where one can communicate and share experience (information), and where, as a result of communication, everyone’s information security increases. Socialization allows the exchange of information between people, there is a possibility of division of labor, leading to a multiple increase in productivity, to an increase in the wealth (resources for development) of society.
Thus, the emergence of sufficient intelligence in the HS makes it possible to use an information resource that has such a remarkable property.
The reasons for the emergence of cultural evolution
Not upright posture of a person, i.e. the movement of a person on two limbs, and not work made Homo sapiens a person, as they write about it
evolutionists are philosophers. These are only accompanying factors of this metamorphosis.
Two factors made cultural evolution possible:
1. A developed mind and advanced communication languages created by it, which made it possible to work effectively with information.
2. The property of an information resource — when sharing it with others, it does not diminish in the original owner.
Man has managed, living in relatively small communities of hunter-gatherers, to create developed languages of communication, and his mind made it possible to extract useful information from everyday experience and systematize. For example, the mind suggested that it is possible not to roam, collecting prey and hunting, but to live in one place, raising what is possible, domesticating animals and raising livestock. The creation of relatively large settlements revealed the benefits of cooperative interaction, because in such settlements, the division of labor, the exchange of information is already possible, and the protection against possible aggressive actions of the neighboring population increases.
Languages of communication were the tool allowing to own, use, exchange information.
Correct division of labor
The variability of species discovered by Charles Darwin extends to the species Homo Sapiens. Only a small percentage of gifted people in societies are able to extract information and dissect it in the brain so that it turns out to be useful for the life of not only them, but a significant number of people. Therefore, large agglomerations are needed, in which there will be a certain number of such people.
The wealth of peoples is not in the accumulated gold, it is in the technologies mastered, in the ability to develop innovations, in the division of labor, in the correct use of the information resource.
A team of creative people is needed for innovation. It cannot be done alone.
The correct division of labor means that it is Archimedes (people of this kind) who thinks, invents, learns, Hercules performs feats, the Macedonian conquers India, Abram and Joseph as the most wise, compose religious texts that are supposedly dictated from above, and the common man works hard with their qualifications. And everything starts to develop rapidly due to the cooperation of efforts. But this is ideal. This is not exactly how it happens in life.
But it is still clear that in a large community there should be more smart, gifted people. And if one of them invents the wheel, the idea of the wheel becomes common property, and today the whole world is already on wheels. But there was someone first who came up with it.
In A. Tvardovsky’s «Vasily Terkin» this idea about innovation in relation to the field kitchen in the war is formulated as follows.
Smart, to be sure,
There was the same old man
What did the soup come up with
On wheels straight.
To use the information resource and share it, they need some trust in large societies.
Homo sapiens had a significant obstacle on the way to socialization. This is intraspecific aggression. It is justified, is an adaptation, to the conditions of existence in ancient times, when every stranger on the territory of the tribe was considered an enemy and was subject to exile, since the territory provided the tribe with food, just like now it is happening in the animal world.
Overcoming intraspecific aggression

On the trajectory of biological evolution, HS was retained by those adaptations that had been developed in previous periods.
Genetic adaptations are always a modification of the genome to the previous environmental conditions and in this sense they are obsolete, since the environmental conditions themselves change over time.
So, for example, in Africa, the homeland of HS, lions still live in prides, marking their territory. Any lion who invades someone else’s territory is considered by the leader of the pride as an enemy that must be expelled or destroyed. After all, the habitat is a matter of feeding the pride.
Likewise, the ancient hunter-gatherers considered the enemy of any HS located on their territory that did not belong to their family. This is where aggression is needed to destroy or expel a stranger.
We must understand that this behavior is genetically determined, we can even say that this is a genetic adaptation, which also sits in our genes in a somewhat softened form. This adaptation manifests itself as an instinct that creates a certain pattern of behavior.
Even in recent times, primitive people not only killed their enemies, but did it with special cruelty — they buried them alive, scalped them, and so on. They did it without any apparent need, by order of their primitive instinct. Such behavior is described by Charles Darwin, who observed how the natives on Tierra del Fuego were killed by the colonists simply because «they quickly multiply.»
Consequently, in order to overcome (restrain the innate instinct) of aggression, it is required to create in the brain some moral prohibitions that block this instinct. It is necessary to change the mentality of a person by changing the functional state of individual brain nodes in the process of education. Religions have served this purpose.
Therefore, in the religious information about the «correct faith», in addition to information about the structure of the universe, there was also information of a certain moral ethical nature. The examples showed how to behave in a society of their own kind and described the punishments that, in the event of violation of these moral standards, will be imposed on the guilty person after his death on this Earth. Life was supposed to be eternal, and the soul was immortal, so punishment is a serious punishment. Among these moral prohibitions was, as a rule, the principle of «Thou shalt not kill.» Religion has turned out to be an important institution of influencing the mentality of people in the sense of restraining aggression towards their own kind.
The introduction by the primitive religion of some moral norms and rules of human behavior in various situations, the creation of some general rules of prohibition, was very important for life in a social society.
Without these rules, as experience shows, the relationship turned out to be prohibitively cruel, and there could be no talk of any cooperation.
God or gods are present in all religions, but they are not the essence of religions. They should be viewed as a way of bringing religious knowledge from somewhere above, from a cult figure, so that believers do not even have a thought to challenge or modernize them. The fact is that the process of replicating information in the brain is not nearly as accurate as the process of DNA replication. Here, to make it more accurate, we need inaccessible gods in religions. They have no other functions. To confirm this thought, you can recall the game «Broken Phone», where after several replications, the information changes beyond recognition.
By introducing into the consciousness of religious rules of behavior that limited aggression, providing for punishment for violations of prescriptions, apparently, it was possible to curb this genetic adaptation to a significant extent (Aggression to a stranger). Note, not to destroy, but to curb, because we cannot rebuild the genome. And genes create innate instincts as a result of a cascade of sequential biochemical reactions that affect the nervous system and brain. There are no patterns of behavior directly in the genes; only the rules for constructing proteins from the 20 available amino acids are fixed in them.
Aggression is still bubbling inside us today, and the way out for it is blocked to one degree or another by moral prohibitions in the brain. It is costly to contain these emotions in terms of physical health. You have to pay for everything. But the payoff is greater. At this stage of the transition of the population from the existence of tribal tribes to the existence in the form of large agglomerations, where the individual’s aggression must be somehow curbed, religion has played, apparently, a significant role.

The same position on the unification of people (socialization) is held by the philosopher and economist of the liberal trend, Nobel laureate Friedrich Hayek in his work «Pernicious arrogance».
Quote.
«Often these rules (morality) forbade the individual to perform actions dictated by instinct. Forming actually new and different from the previous morality, they restrain and suppress «natural morality», that is, those instincts that rallied the small group and ensured cooperation within it, blocking and making it difficult to expand.
However, the decisive factor in the transformation of an animal into a human was precisely the curbing of innate reactions caused by the development of culture.
The norms and habits learned in infancy become as much a part of our personality as that which was already guiding our behavior when the assimilation was just beginning.»
5. Replicators of culture
Human cultural evolution is an observable fact. It must have mandatory attributes like any evolution of living things. Therefore, it is required to indicate its replicators and inheritance mechanisms, since the corresponding attributes of biological evolution (genes) cannot explain the fact of cultural evolution.
Sociobiology studies the phenomenon of human cultural evolution from a natural scientific standpoint. It can be presented as an attempt to penetrate the scientific approach into the area where the humanities now dominate. The humanities do not need to justify the very existence of cultural evolution, they just need to postulate it. But science seeks to reduce the number of postulates to a minimum. If you postulate something, then there is no need to prove it and explain it. Naturally, sociobiology encounters powerful resistance from the humanities and those who have joined them, since it deprives them of their daily bread (and not only).
Sociology, important for practice, developed exclusively on an empirical basis, must follow from sociobiology, as chemistry does from physics. As far as history, biographical and fiction books are concerned, they should be viewed as research protocols for sociology.
Replicators by R. Dawkins
The idea of replicators of culture was expressed by R. Dawkins. Clinton Richard Dawkins (March 26, 1941) — English ethologist, evolutionary biologist, scientist and popularizer of science

Dawkins has become widely known since 1976, when his book «The Selfish Gene» was published, in which the term «meme» was introduced into the lexicon, denoting a unit of cultural information that is copied and transmitted from one carrier to another and is subject to mutations, natural selection and artificial selection.
Dawkins writes: «All living things evolve as a result of the differential survival of replicating units. It so happened that the gene — a DNA molecule — turned out to be the dominant replicating unit on our planet.
It seems to me that a new type of replicator has recently appeared on our planet. It is still in childhood, still floundering awkwardly in its primordial soup, but evolving at such a rate that it leaves the good old gene far behind.
The new broth is the broth of human culture. We need a name for the new replicator, a noun that would reflect the idea of a unit of cultural heritage transmission or a unit of imitation. A suitable Greek root gives the word mimem, but I want the word to be monosyllabic, like gene. I hope my classically trained friends will forgive me if I shorten mimem to meme.
In Dawkins’ replicator-idea, propagated by imitation. There is a lot of unsaid in this definition. Let’s assume that Dawkins only set the task of finding a certain entity that would satisfy the set task — to be a replicator in cultural evolution.
If it was possible to find a cultural replicator and mechanisms for its transmission in generations, then it would be possible to build a theory about human behavior in societies, reminiscent of population genetics.
Бесплатный фрагмент закончился.
Купите книгу, чтобы продолжить чтение.