
Бесплатный фрагмент - Marketing and Pricing
Автор-составитель: БОНДАРЕНКО Валерий Семенович, доцент, кандидат географических наук (экономическая, социальная, политическая география). 2017 г.
Данный курс лекций предназначен для студентов и магистрантов, изучающих часть предметов на английском языке. Курс лекций составлен на основании учебной программы и образовательных стандартов для экономических специальностей УВО: «Мировая экономика», «Бухгалтерский учет и аудит», «Экономика предприятия», «Финансы и кредит». Данное пособие рассчитано на учащихся, чей уровень владения английским языком соответствует уровням Elemantary или Pre-Intermediate, то есть когда уже освоен уровень Beginner.
Курс лекций включает 14 лекций, каждая из которых отражает отдельную тему курса «Маркетинг и ценообразование». Курс лекций апробирован в практике учебного процесса в ряде УВО Беларуси и России. Каждая лекция (тема курса) данного пособия завершается краткими выводами и/или вопросами для повторения, которые также могут быть использованы в учебном процессе как тематика рефератов или докладов, по согласованию с преподавателем.
В списке рекомендованной литературы приведены основные источники на русском языке. Выбор англоязычных источников зависит от конкретных целей учащегося, а также от его уровня владения английским языком. Напоминаем, что структура и содержание учебников, изданных в США и Великобритании соответствует требованиям и программам университетов и колледжей этих стран, и потому существуют значительные отличия от российских и белорусских программ и учебников, а также от учебников других стран СНГ.
В пояснительной записке (explanatory note), помещенной в начале курса лекций, сформулированы (на английском языке) основные цели и задачи учебной дисциплину, а также основные компетенции, которыми должен обладать магистрант и которые формируются в учебном процессе с помощью данного курса лекций.
CONTENT
Explanatory note
SECTION 1. MARKETING
THEME 1. MODERN CONCEPT OF MARKETING
1. Marketing as a business philosophy
2. Basic concepts and scope of marketing
3. The principles of marketing and its functions
4. The structure of (complex) marketing
THEME 2. MARKETING RESEARCH
1. Marketing information system
2 The essence of marketing research
3. Market research
THEME 3. CONSUMER BEHAVIOR AND CUSTOMERS
1 The behavior of buyers in the consumer market
2. The behavior of buyers in the market enterprises
3. Consumer protection
THEME 4. COMMODITY POLICY
1. The essence of commodity policy
2. The essence of the product and its classification
3. Trading range and variety of products
4. The process of developing new products and planning their life cycle
THEME 5. DISTRIBUTION POLICY
1. Purpose, Structure and function of the distribution system.
2. Types of distribution channels
3 Management of the distribution channels
THEME 6. PROMOTION POLICY
1.The essence of communication policy
2. The main tools of communication policy
3. Budgeting and performance evaluation of communication policy
THEME 7. Department of Marketing
1. The essence of management based on marketing
2. Marketing planning
3. The organization of marketing in business
4. Control of marketing activities
SECTION 2 PRICING
THEME 9. THEORETICAL BASIS OF PRICING
1. The evolution of the theory of pricing
2. The concept of pricing in the Republic of Belarus
3. Pricing policy
THEME 10. PRICES IN THE MECHANISM OF THE ECONOMY
1. The economic content of prices.
2. Factors that impact on prices.
3. Price system
4. Classification of prices.
THEME 11. State regulation of prices in the Republic of Belarus
1 The need for state regulation of prices
2. Methods of state regulation of prices: indirect and direct
3. The policy of state regulation, carried out in the Republic of Belarus
4. Antitrust laws
THEME 12. METHODS AND PRICING STRATEGY
1. Pricing methods based on production costs
2. Methods of pricing, quality-oriented and consumer product properties
3. Methods of pricing, demand-driven, the level of competition
4. Market-based pricing strategy
THEME 13. PRICES IN ECONOMICS OF BUSINESS
1. Selling price of the enterprise and the order of its formation
2. Features of pricing in the market of consumer goods and services
THEME 14. PRICING IN MARKETING COMPANY
1. Technology justify prices in the marketing business
2. The information needed to make decisions on prices
3. Study of consumer response to price changes
Literatures
EXPLANATORY NOTE
A postgraduate of degree «Master of Economics» must have the following competences:
academic competences — science, theoretical, methodological knowledge and research skills providing elaboration of research projects or solving tasks for scientific research, innovative activity, continuous self-education;
social and personal competences — personal qualities and skills for following social, cultural, and moral values, social responsibility;
professional competences — skills and abilities to solve complicated professional problems in research and educational activity, to elaborate and adopt innovative projects.
Master should be able to:
To generate new ideas.
To acquire new knowledge and skills independently, including the areas of knowledge that are not directly related to the field of activity.
To take the initiative, including the situations of risk, to take responsibility, to resolve problem situations.
The requirements are for Master’s social and personal competencies
Master should be able to:
To be able to take into account the social, moral and ethical standards in social and professional activities.
To be able to cooperate and work as a team.
To use one of the state languages of the Republic of Belarus and any foreign language as a means of business communication.
To generate and argue personal judgment and professional position.
To use logical, reasoned, clear oral and written language, to use the skills of public speaking, conducting discussion and debates.
To work as a team, to lead and to obey.
To respect and protect the historical heritage and cultural traditions, to perceive social and cultural differences tolerantly.
To take the initiative and creativity, including unusual situations.
To adapt to new situations of social and professional activities, to implement the experience, possibilities.
The requirements are for Master’s professional competence
Master should be able to:
Organizational-administrative activity
Assess the process taking place in international economy, identify trends and prospects.
Analyze and develop recommendations to improve the national development strategy.
Use elements of economic analysis in organizing of practice in the workplace.
Translation activities
To possess modern means of telecommunications.
To keep professional, social and cultural communication in a foreign language.
The implementation of these competences while studying the course «Current Global Issues» envisages the following tasks:
knowledge and understanding of the concept «global issues»;
awareness of existing global problems;
having deep information about main historical events and tendencies which lead to the emergence of global problems;
analyzing current world political, economic, social, and cultural developments;
understanding the essence and main directions of globalization process, its positive and negative aspects;
understanding the essence and content of the main current global issues;
realizing interconnections and interactions between global problems and national and world economies state and trends of development;
knowledge of the role and activities of international organizations for overcoming global issues.
knowledge of the contents of main international programs for solving global issues;
realizing manifestations of global issues in native countries of a student;
skills and willingness to make personal contribution in overcoming global problems after taking position according to obtained degree.
As a result of the discipline studying the master’s students should
know:
— the subject and methodology of the discipline;
— concept and evolution stages of the world economy theory;
— structure and development trends of the world economy;
— concept of the international division of labour, its special aspects in current conditions;
— subject-matter of internationalization, transnationalization and globalization;
— substance of international economic integration and its forms, special aspects of integration process in the world economy;
— content of international currency relations and their components;
— up-to-date theory and practice of macroeconomic regulation in open economy.
be able to:
— estimate processes taking place in the world economy;
— determine development trends and prospects for countries, groups of countries and the world economy;
— analyse position of the country in international division of labour, degree of openness of an economy;
— use concepts of the international division of labour and international trade;
estimate critically conditions of foreign economic relations and determine advanced directions for national economy participation in the world economic relation.
SECTION 1. MARKETING
THEME 1. MODERN CONCEPT OF MARKETING
1. Marketing as a business philosophy
At the core of the term «marketing» is the word «market», which means «the market.» So, in the marketing one often understands the philosophy of governance, economic conditions in the market, proclaiming the orientation of the production to meet the needs of specific customers.
Marketing under its widest sense is a social and managerial process by which individuals and groups of people get what they need by creating products and exchanging them. When a person is unable to meet any need, he substitutes them or reduce the level of his requests.
EVOLUTION OF MARKETING
Phase Period Characteristics
I. beginning the twentieth century — 40th
Marketing had a sales character. The motto: «Everything produced must be sold». Sales methods of marketing and advertising were applied
II. 50 years — first half 70s
Marketing has been focused on the study of the market and customer demands.
The principle is: «It is advantageous to produce the products that will be in demand than to produce something that struggles to sell.»
III. second half 70’s — till present
Integrated market system covers the entire cycle of development, production and sale of goods, including market research, implementation of merchandise, pricing, communication and policy, strategic marketing governance and other marketing techniques
Thus, the requirements are translated into specific desires, which in view of monetary opportunities are transformed into market demand on the specific products. It appears the exchange between producers and consumers made out in the form of a particular transaction. It follows that the direct marketing economy to meet the constantly changing needs of the many millions of consumers.
In other words, the marketing is a philosophy of management, direction of its implementation, when the resolution of consumer problems leads to the success of the organization and brings benefit to the society.
At the level of individual economic entities marketing is defined as a complete system for planning the variety and quantity of produced products, pricing, distribution of products between the chosen markets and to promote their sales in order to achieve the diversity of benefits, led to the satisfaction of the interests of both producers and consumers. This definition has a sufficiently broad sense, as it covers the activities of non-profit organizations. Thus, marketing is the activity of the organization for the benefit of its customers.
In a more narrow sense (entrepreneurial) the marketing can be classified as a management system of production and sales management organization aimed at obtaining an acceptable value profit through accounting and active influence on market conditions.
From the above it follows that a variety of marketing applications causes a variety of its definitions.
It seems that as a fairly general definition of marketing can be offered. Marketing is a form of human activity to meet the demand for the material and non-material, social, value through mutually beneficial exchange.
Thus, marketing is also a system of thought and action system.
2. Basic concepts and scope of marketing
The concept of needs is at the core of theories of motivation (Freud, Maslow, etc.), determining the behavior of consumers in the market. The main task of marketing is to find a need and meet it.
Desire is the need to take concrete shape in accordance with the level of culture and personality of the individual. Sometimes it is called concretized need. For example, the total demand for food is transformed into a more private demand in the fruit, which, in turn, concretized results in the need, the desire to buy apples.
Demand is a desire, a specific need, backed by purchasing power. For given resource capabilities people satisfy their needs and desires through the purchase of goods that bring them the greatest benefit and satisfaction.
Product is all that can be offered on the market for the acquisition, use or consumption in order to meet specific needs.
Product is all that can satisfy any needs (physical goods, services, people, organizations, activities, ideas). In the literature on marketing the English term «product» is often translated as «goods». It is understood that the product manufactured by the manufacturer, with translational division by becoming a commodity market.
Exchange is the act of obtaining a desired product from someone by offering him something in return. Exchange is just one of the many ways means of which people get the desired product. Another way is hunting, gardening. This includes theft and begging.
The deal is trading between the two sides, including at least two subjects of interest and agreement on the terms, timing and months, those of its implementation. There are two types of transactions: cash transaction when goods are exchanged for money and barter transaction. The deal involves the performance of the following conditions: the presence of at least two products representing the interest for the mutual exchange, the agreed conditions, time and place of its commission.
The market in the marketing sense is a collection of existing or potential sellers and buyers of any products; it’s a place where deals are made. It is on the market the manufactured product and labor on it expended prove their social importance, acquire recognition among consumers. In modern society, the market does not necessarily have a physical location. To demonstrate the product, its advertising and getting the orders modern means of communication, without physical contact with customers are widely used. (In marketing, the market is the set of consumers of a particular product, they say, the market of metal, grain, etc. On the basis of this principle market segmentation is often carried).
3. The principles of marketing and its functions
There are the following marketing principles:
1. Careful consideration in deciding the needs, conditions and dynamics of demand and market conditions.
Adherence to this principle requires a good knowledge of the market situation and on the existing estimates of expected demand, activities of competitors in the market, the market behavior of consumers and of the ratio of the products of this company and its competitors.
2. Creating the conditions for maximum device production to market demand, the structure of demand based not on short-term gain and long-term perspective.
The modern concept of marketing is that all activities of the company (scientific, technical, manufacturing, marketing, etc.) were based on knowledge of consumer demand and changes in perspective.
3. To inform potential customers about the products and the impact on the organization of consumers using all available means, first of all advertising, in order to induce them to purchase exactly the product.
The marketing function
Formation of Trade Policy
— The development of the concept of commodity
— Formation of assortment;
— Taking into account the life cycle of the goods;
— Competitiveness;
— Creation of product attributes;
— Development of new products, etc.
Implementation of the marketing policy
— The definition of the concept of marketing;
— Select the channel distribution;
— Formation of distribution;
— Control of product distribution processes, etc
The organization of communication policy
— The organization of advertising;
— Public Relations;
— Personal selling;
— Sales promotion, etc.
Strategic management of branding
— Planning of marketing activities;
— The organization of the service brand-Thing;
— Control of execution, etc.
4. The structure of marketing complex
According to Kotler marketing complex is a collection of allowing controll marketing variables, the set of which the company uses in an effort to induce the desired reaction on the part of the title of the market.
The components of the marketing complex are:
• Trade policy.
Product is a set of «goods and services», which the company offers to the target market. Thus, a new painkiller could be a «commodity» in the form of a 50 white tablets in a white bottle with a cap that cannot close the children of, a three year shelf life, branded name «Aveline» and a money back guarantee in case of dissatisfaction with the buyer.
• Communication policy (sales promotion).
Methods of incentives are all sorts of activities of the company in order to spread information about the merits of the goods and to convince consumers to bathe in it. The company pays advertising, hires salespeople pushes the product with special events, organize its propaganda.
• Sales Policy.
Methods of distribution are all sorts of activities, through which product becomes available to target consumers. Thus, the firm chooses wholesalers and retailers, to convince them to pay for the goods more attention and care for the good of his computation, it looks the over-passes and provides efficient transport and storage.
• Pricing policy.
Price is amount of money that consumers have to pay for the obtaining of goods. The company offers retail and wholesale prices, favorable prices and discounts, sales on credit. The price should correspond the perceived value of the offer, otherwise buyers will acquires competitors’ products.
This structuring of the (complex) marketing fits into the concept of «4P», according to which in the marketing complex includes 4 elements, the name of the English language which begin with the letter «P»: product, promotion, place, price.
THEME 2. MARKETING RESEARCH
1. Marketing information system
In a well-functioning organizations marketing information is collected, analyzed and distributed as part of a marketing information system (MIS), which is part of the management information system of organization.
MIS concept originated in the United States, where it was put into implementation in the early ’70s, a few years after the development of the concept of an automated control system (ACS) in the case of individual-governmental organizations.
MIS is a collection (single set) of personnel, equipment, procedures, and methods for collecting, processing, analysis and distribution of the set time reliable information necessary for the preparation and making marketing decisions. It is sometimes said that the MIS is a way of thinking through solutions to find the necessary managers frames marketing information. It is recognized that the leaders and specialists of marketing are in need of specific information and the methods of its receipt. Thus, the MIS — is a conceptual system that helps to solve the problem of how marketing and objectives strategic planning.
The scheme of a marketing information system is as follows:
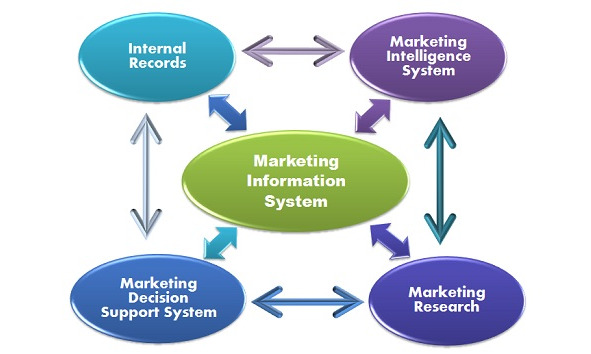
According to Philip Kotler, the four components that comprise the MIS are Internal Reports (Records) System, Marketing Research System, Marketing Intelligence System, and Marketing Decision Support System.
1.Internal Records: It records various data from different department of a company, which is regarded as a major source of information.
2.Marketing Intelligence System: It is a main source used by managers for gaining daily information of the external environment, hence assists the managers to react to the changing rapidly.
3.Marketing Research System: It is used to collect primary and secondary data, and displays the results in forms of reports.
4.Marketing Decision Support System: Compared to the supply of the data by the three previous systems, it focuses more on processing the data.
MIS transforms data from internal and external sources into information necessary for managers and professionals’ marketing services. MIS distributes information to managers and specialists of marketing services, taking appropriate decisions. In addition, ISI, interacting with other automated systems in the enterprise, delivers the right information managers of other services enterprises. Internal information contains data on orders for products, sales, shipment of goods, the level of reserves, the payment of shipped products. Data from external sources are obtained on the basis of market intelligence and market research.
Marketing intelligence is a constant effort to collect the current information about changing marketing environment necessary for the development and adjustment of marketing plans. While inside information focuses on the results obtained, maketing intelligence explores what might happen in the environment.
The sources of the current external information can be of different nature, for her collection formal and informal procedures are used. Such information is obtained through the study of books, magazines, trade publications, reports of competing firms, as a result of conversations with customers, suppliers, distributors and other external to the organization of parties, which should be effectively motivated on the collection and provision of the necessary information; based on conversations with other managers and employees, for example, employees of marketing services of the organization, through industrial and commercial espionage (although in many foreign books written about the ethical issues of marketing research).
Primary information is generated in the process of data collection methods to address a specific problem. It is necessary when secondary data are insufficient in terms of their completeness and values.
Secondary information is the data obtained from the accounting and statistical reporting, special publications, directories, i.e. information collected for another purpose.
2. The essence of marketing research
Market research presupposes the collection and analysis of data on specific marketing situations with which the company has faced in the market. Such activities are carried out periodically, rather than continuously, as soon as certain problems on the basis of the use of special methods for collecting and processing the data collected.
Depending on the nature and purpose of market research three relevant areas are identified (exploratory, descriptive and casual). Any such direction includes certain methods of collecting and analyzing marketing information.
Exploratory research is a marketing research conducted to gather preliminary information needed for a better definition of the problems and put forward suggestions (hypotheses), in which implementation of marketing activities, as well as clarifying the terminology and setting priorities among the tasks of research is expected.
Descriptive research is a marketing research aimed to describe marketing problems, situations, markets, for example, the demographic situation, consumers’ attitudes toward the company’s products.
Causal research is a market research conducted to test hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships.
Under the experimental research is meant collecting primary data by selecting the same type of groups surveyed, the issuance of different tasks, monitor the factors that affect the results and comparison of the differences in group responses.
Marketing research process includes the following steps and procedures:
1. Defining the problem and research purposes.
1.1. Determining the need for market research.
1.2. Problem definition and formulation of marketing research purposes.
2. The development of the research plan.
2.1. The choice of methods of marketing research.
2.2. Determining the type of information required and the sources of its receipt.
2.3. Determination of methods of collecting the necessary data.
2.4. Development of a questionnaire to collect data.
2.5. Development of sampling plan and determination of sample size.
3. The implementation of the research plan.
3.1. Data collection.
3.2. The analysis of the data.
4. Interpretation of the results and bring them to the leadership (preparation and presentation of the final report).
3. Market research
Marketing research involves, as a rule, all the elements of the outer and internal business environment of a business entity. However, very often all sorts of circumstances hamper the comprehensive study of marketing, but there are a number of positions, which in any situation should be transparent to the manufacturer. Among them, first of all, can be distinguished: market demand, capacity and market share, especially of consumer preferences and market segments for consumer goods and industrial goods. In this regard, we will try to consider them in details.
When an organization or company decides for itself the choice of the target segment, target market, it is based, first of all, on market demand.
Market demand is the total amount of sales in a particular market and particular brand product for a certain period of time.
Market demand can be classified on the basis of the dependence of demand and marketing efforts:
primary or unstimulated demand is the total demand for all brands, under which a particular product is sold in a particular market without use with any marketing efforts;
market potential is the maximum amount seeking by the market demand at the approach of marketing costs in the industry, productivity certain product, to a value at which its further growth does not lead to an increase in demand for the product. The magnitude of this type of demand has significant impact environmental factors marketing organization or company;
current market demand is sales volume of a particular product for a certain period of time under certain environmental conditions, and at a certain level of use of marketing tools.
In determining the amount consumed, sold goods in a particular period of time of production one must consider this situation not only with terms of consumer behavior, but also the point of view of the manufacturer. In the latter case, often use the term «the real size of the market,» or simply «the capacitance of the market», which is defined the potential annual sales of a certain kind of product at a certain price level.
Speaking directly about the method of determining the capacity of the market, you should immediately call attention to the fact that this measure can be carried out on the basis of statistical information on the volume of production and sales in a particular period of time, taking into account the share of imported from abroad and exported abroad goods of this type.
C = P + R-E + I + D-M-E0 + I0,
where C — the capacity of this market;
P — domestic production of the commodity in the country;
R-remnant inventory in warehouses in the country;
E — exports of goods;
I — volume of imports of the product;
D — reduction of inventory from the seller;
M — an increase in inventory from the seller;
E0 — indirect exports;
I0 — indirect imports.
However, this method has a large proportion of errors due to the imperfections of the existing statistical reporting system. Especially this applies to those commodity markets where a large amount of wholesale and retail intermediaries operate who often distorts to conceal income, the data on the volume of production, sales and revenue.
Among other approaches to determining the capacity of the market we would like to stay on the normative. It is based on the use of consumption norms of certain goods, the sales data, the number of customers and frequency of purchases etc.
In general, the definition of the current market demand (real capacitance of the market) in monetary terms is as follows:
Q = n * q * p,
where Q — the current market demand in terms of money;
n — number of buyers of this type of product in the market;
q — the number of purchases of goods, accounting for one customer in the monitoring period;
p — the average price of this product.
Naturally market capacity calculation by using this method also has a certain degree of error. In this regard, for a more accurate calculation can be implemented in phases, breaking the totality of consumers buying into smaller segments, having more specific characteristics. For example, conducting research market of meat products, consumers can be divided into several segments according to age, believing that the average rate of consumption of meat products vary depending on the age of the consumer. This specification will provide more accurate indicators of the separate to customer segments that have a positive impact on the results of the determination of the total market volume. Natural disadvantage of this method is the difficulty with the definition of the relevant regulations and partitioning on consumer segments. In addition, all the errors that occur in the calculation of interim standards and indicators are reflected in the final result. To avoid this problem, one must use a few different techniques and then find the average value.
To have a more detailed approach to the problem of the study of market demand, it is necessary to study the impact on sales and consumption of such factors as: price, income, consumption patterns, etc. The above approach can also be used to predict the demand.
THEME 3. CONSUMER BEHAVIOR AND CUSTOMERS
1. The behavior of buyers in the consumer market
Purchasing behavior (concumer buying) is the buying behavior of individuals or families who acquire goods and services for personal consumption.
Every day consumers make a lot of decisions what to buy. Most large companies explore the process of making decisions about the purchase, to find out what, where, how and how much, when and why consumers are purchasing. Marketers are also studying this process, but they are interested in the answers to the questions what, where and how much.
However, to reveal all the secrets of buying behavior is very difficult, because the reasons for decisions are often hidden away deep in the consumers subconscious.
The main issue of marketing is how different buyers react to marketing techniques? The company who really understands how consumers react to the different qualities of the product, its price and advertising, gets a significant advantage over competitors. The starting point is a model of consumer behavior «motivation — reaction». It is clear that marketing and other incentives penetration-cabins in the «black box» of the consumer and generate a response. Marketers need to find out what is hidden in the «black box.»
Consumer market are individuals and families who purchase goods and services for personal consumption.
Marketing stimuli consist of the four elements, the so-called «Four P»: product, price, place and promotion. Other factors depend on the environment surrounding the buyer: the economy, technology, politics and culture. All of these components fall into the «black box» of the consumer and are converted into an aggregate of the observed reactions: product selection, trademark, trade an intermediary, the time of purchase and the purchase volume
The buyer’s choice is heavily influenced by cultural, social, personal and psychological factors. Although the marketer cannot affect on many of them, but by using them, it can determine the interested buyers and simulate product to meet their needs better. Marketers need to approach the process of analyzing user behavior with extreme caution.
Most companies are scrutinizing the process of deciding whether to buy in order to answer the following questions: what, where, how, how much and why consumers buy. Marketers can study consumers purchasing to answer questions about what is bought, where and how much. But the study of the causes of consumer behavior and the process of adoption of solutions is not an easy process, as the full answers are hidden in the consciousness of the consumer.
Now we are ready to consider the steps that take place when the buyer is in the purchase decision. The are five stages: awareness of the needs, information search, evaluation of options, the decision to purchase and reaction to purchase. It is obvious that the process begins long before the purchase factor is the acquisition and does not end this moment. Marketer has time to understand the process as a whole and not focus solely on the decision.
In theory, the buyer goes through all five stages at each sell. However, in practice, the consumer is often missing or reverses some stages. A woman who regularly buys the same brand of toothpaste, after realizing the problem will immediately jump to the decision to purchase, skipping stages of information search and evaluation of options. But we use the model shown in Fig. 3.3, since it reflects the logic of the consumer when he gets into a new and difficult situation.
We reviewed the steps that the buyer passes, trying to satisfy their needs. Speed of these stages varies; some of them can be omitted. Some of them may even be reversed. Much depends on the nature of consumer goods and the purchase situation.
Now we will see how the buyer acts in choosing new items. Product-novelty is a product, service, or idea perceived by potential buyers as something new. Commodity novelty is not necessarily a brand new on the market and each product can be a novelty for the buyer, who previously did not know about it. Therefore, we are interested in how the consumer finds out about it for the first time and how comes to a decision about whether to buy it. Decision process is understood as a «thinking proces through which a person from the moment when he heard about the new product for the first time, until its full adoption» and the adoption is a solution of the person to become a user of goods.
New product is the product, service or idea, perceptible by a potential buyer as something new. The adoption process is the thought process from the moment when the buyer first heard about the new product, until its full adoption.
To adapt to the new product buyer needs to take five steps:
1. Recognition. The consumer learns about the new product, but has little information about it.
2. Interest. The consumer is looking for information about a new product.
3. Evaluation. The user determines whether to acquire the product.
4. Sample. The consumer closer acquainted with the goods in order to gain a more complete understanding of it.
5. Perception. The consumer decides on a regular basis and always uses a new product.
This model assumes that the marketer engaged in product-innovation should think about how you can help the consumer at each of these stages. Suppose a company — manufacturer of televisions with a large-screen TV recognizes that many consumers, although it had an interest in its products are in no hurry to move to the stage of trial, because they do not believe in the advantages of the new model and do not want to pay the higher price. However, the same customers for a small fee gladly took a new trial on television. Hence, the manufacturer must develop a system for transmitting television temporary (trial) use with the possibility of further purchases.
Бесплатный фрагмент закончился.
Купите книгу, чтобы продолжить чтение.